Written by The New Western Team
New Western is committed to delivering opportunities to aspiring investors and keeping them well-informed with timely and relevant content that follows strict editorial integrity.
We often get questions from aspiring investors asking us how to finance an investment property simply because there’s so much information to sift through.
People want to know what are their options, how secure financing, what kind of properties they should start with, and much more.
New Western heard your questions and we want to help. In this extensive guide, you’ll learn about loan options where you don’t need $100k cash, government-funded owner-occupant loans, house hacking, and much more.
Purchasing your first investment property is a huge leap toward generating passive income and getting to the point where you can retire from your 9 to 5 and start living off rental income alone.
However, before you can do that, you need to be 100% certain that you’re ready to make that commitment.
So, how do you know if you’re ready to become a real estate investor?
One of the more common real estate myths is that you need to be employed with the same employer for at least two years in order to qualify for a loan. Yes, steady, long-term employment definitely works in your favor, there are some circumstances where that’s not an option.
The truth is, lenders understand that not everyone will have an extensive work history. Many lenders are willing to work with potential borrowers with a short work history or are just starting a new career. For example:
Ultimately, it is best to find a local accredited lender that will help guide you through the pre-approval process so you will have the confidence in knowing what you can or can’t purchase with a loan.
From Q2 2020 to Q2 2022, real estate prices have increased by 38%, making the median sales price slightly over $440k. If you want to do the traditional 15% to 25% down payment, you’d need to have anywhere from $66,000 to $110,000 saved.
That’s a lot of money, for sure. However, if you expect your tenants to have 3 times the rent (before or after taxes is up to you), then you might want to have at least that much saved as well.
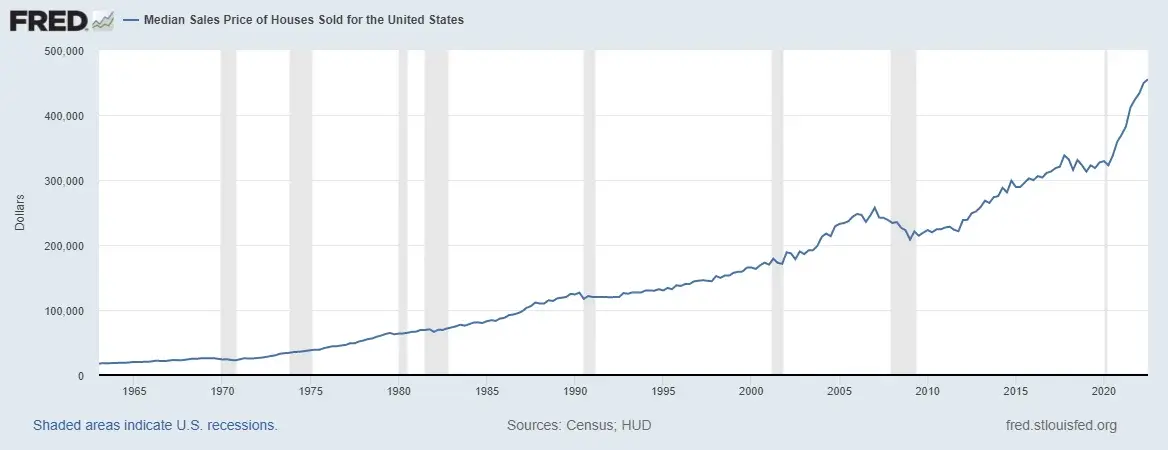
Credit: FRED St. Louis
This money will be used to cover the mortgage, utilities, and insurance, but you’ll also want to have some extra cash for emergency repairs and other unplanned expenses. It’s better to have it and not need it than it is to need it and not have it.
Ask yourself what kind of investor you want to be? Do you want to be involved with the day-to-day operations of a rental property or do you like the idea of having your investments managed by professionals?

"[Indirect investing] offers professional management, assurances for accountability and provides a great way with limited capital to have access to a large pool of properties that offer diversified income from properties located in cities with various economic development opportunities."
"Capital is the most important factor that prevents small investors from having access to good quality properties with many rental units. The indirect investment approach offers even small investors to participate in top quality properties and achieve good risk-adjusted returns."

"Rental properties are one of the most financially viable investment properties. They offer several tax benefits that other types of investment properties may not."
"For example:
Deductible operating expenses such as property management fees, repair, and maintenance, property taxes, leasing commission, advertising, etc. Depreciation deduction Deductible mortgage interest Ability to defer capital gains tax Avoid FICA taxes Deductible owner expenses"
"Therefore, the proceeds of the sale should be reinvested. Only experienced investors can navigate the transition to purchasing another property while the sale is finalized."
- Mr. Alex Capozzolo, the co-founder of Brotherly Love Real Estate
Although real estate prices have skyrocketed, there are still good deals out there — you just need to know where to look and how to spot them. If you’re on a budget, distressed properties aren’t the only options you have to find something affordable.
You can find investment properties a number of ways. New Western, for example, is a great resource for finding pocket listings, also known as “off-market” properties for sale. You can join local real estate investor forums to find leads.
If you have found a rental property for sale, don’t sign on the dotted line first because you need to figure out if it’s worth it. There are two metrics that will help you determine if the property is worth the investment: the cash-on-cash return and ROI (return on investment).
Cash-on-cash (CoC) return is an annual measure of an investor’s earnings compared to the amount of money they initially spent to buy it and keep it operational.
To figure out the cash-on-cash return, you have to divide the year’s pre-tax cash flow by the amount of money you’ve invested.

Credit: Avail
You can also use a cash-on-cash return calculator if you prefer.
ROI, on the other hand, is a measure of the property’s overall profitability for however long you own the property.
To figure out the ROI for an investment property, you have to subtract the annual rental income from the annual operating costs. You’ll then want to divide that number by how much is left on the mortgage.

Credit: Avail
You can also use a ROI calculator if you prefer.
As a new investor, it’s a good idea to learn as much as you can about the market you’re interested in.
By conducting a neighborhood analysis, you’re crunching numbers to determine if a certain neighborhood is a good investment or not. It can also be used to help you determine how much you may be able to charge for rent.
Note: A market analysis is comprised of estimates, not actual numbers. While it may not be 100% accurate, it can give you a good idea of what the local market is doing.
The data you’ll want to look at when you’re conducting your analysis should include:

Credit: Elfreth’s Alley in Old City Philadelphia (Lindsay Laraski/WHYY)
According to McKinsey and Company, 58% of surveyed Americans report they’re able to work remotely, either part-time (23%) or full-time (35%). As more industries embrace remote work, be it a hybrid model or fully remote, home prices are likely to continue to rise, according to The National Bureau of Economic Research.
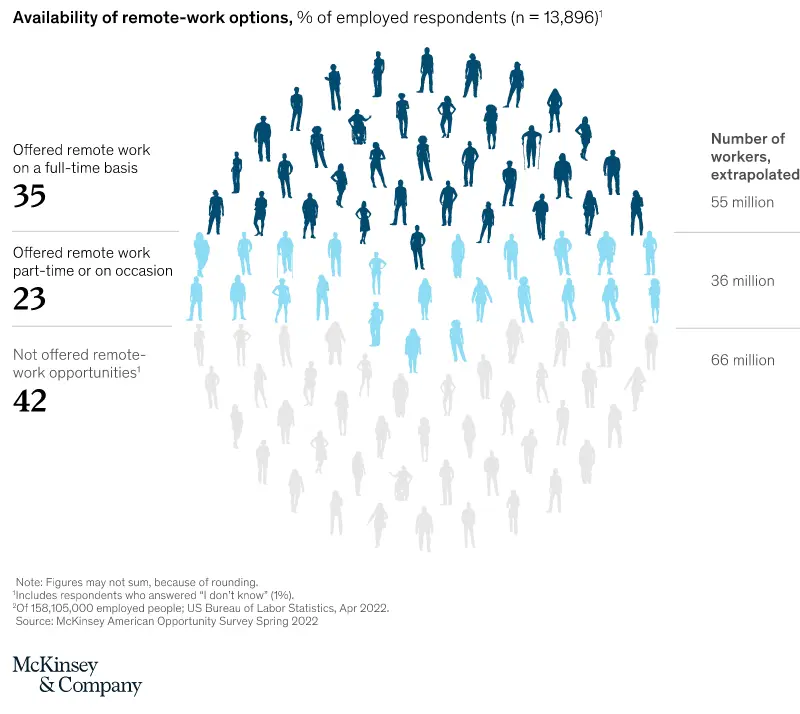
Credit: McKinsey and Company
On one hand, this is good for remote workers who want to move away from the metro areas and relocate somewhere with a lower cost of living. But on the other hand, it could be problematic because when demand goes up, home prices and the cost to rent goes up too.
The FBI Crime Data Explorer is an excellent source to get this information because you can look up data by the state and municipality, as well as specific crime data like specific types of crimes, expanded property crime, hate crimes, expanded homicide crimes and arrests. Unfortunately, you can only see the data up to 2020 and it doesn’t give you a look at specific neighborhoods, just by police departments.
Credit: FBI Crime Data Explorer
AreaVibes is another great source for finding out an area’s crime rate, as well as so much more. You can use the basic search features to sort locations by overall livability score (which uses seven key data points, including crime rate, to determine how desirable a place is), best place to rent, and best place to buy.

Credit: AreaVibes
You can customize your search parameters based on things like population size, cities, cities and neighborhoods, or just neighborhoods, and specific scores for the seven categories shown in the graphic above. This is an excellent tool if you’re trying to find the perfect place to invest.
Other free sources where you can find detailed information (including crime rate) about location include:
If you’ve stumbled across an income property for sale and you want to know if it’s a good deal or not, you’ll want to do a comparative market analysis (CMA).
Step 1: Gather Data About the Desired Property
The data for a real estate CMA can be gathered should include as much detail you can get. If you’re working with a real estate agent, they’ll be able to do this part for you, since they have access to the Multiple Listing Service (MLS).
If you’re doing a CMA on your own, you can use sources like Zillow, Google Street View, House Canary, and county public records. At the bare minimum, you need:
Step 2: Compile Details about the Property’s Previous Sale and Listing Data
This data will help you determine how the market has moved since the last time the property was sold.
For example, let’s say the property you want was sold two years ago when the median price was $322,600, and today’s median price is $440,300. That’s about a 36% increase. Based on this information, it’s safe to assume that the property’s true value has increased by that much.
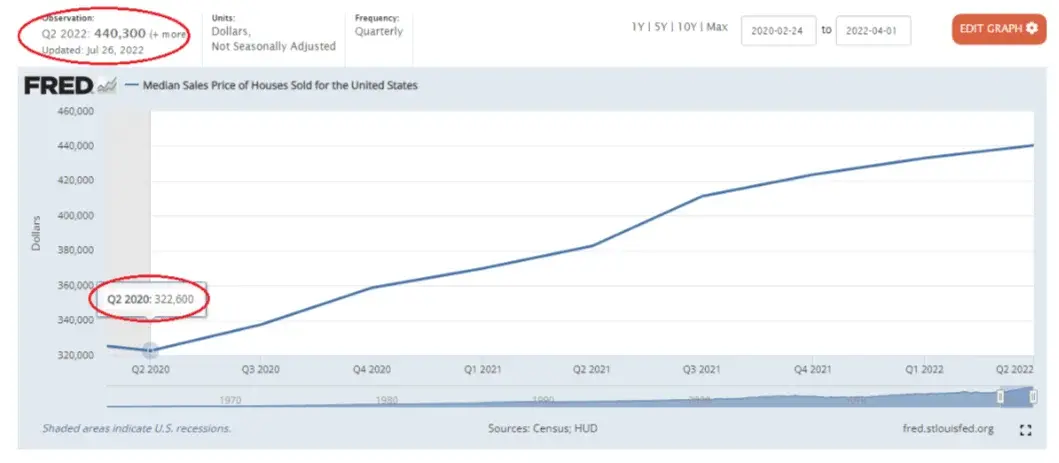
Credit: AreaVibes
You can check this by gathering information about the last time the property was listed and sold. At the bare minimum, you need:
Step 3: Choose 3 to 6 Comparable Properties
Now you’ll need to understand how the property you’re interested in compares to similar properties that have sold in the last six months. When you’re choosing comps, you’ll want to take into account a variety of factors, such as:
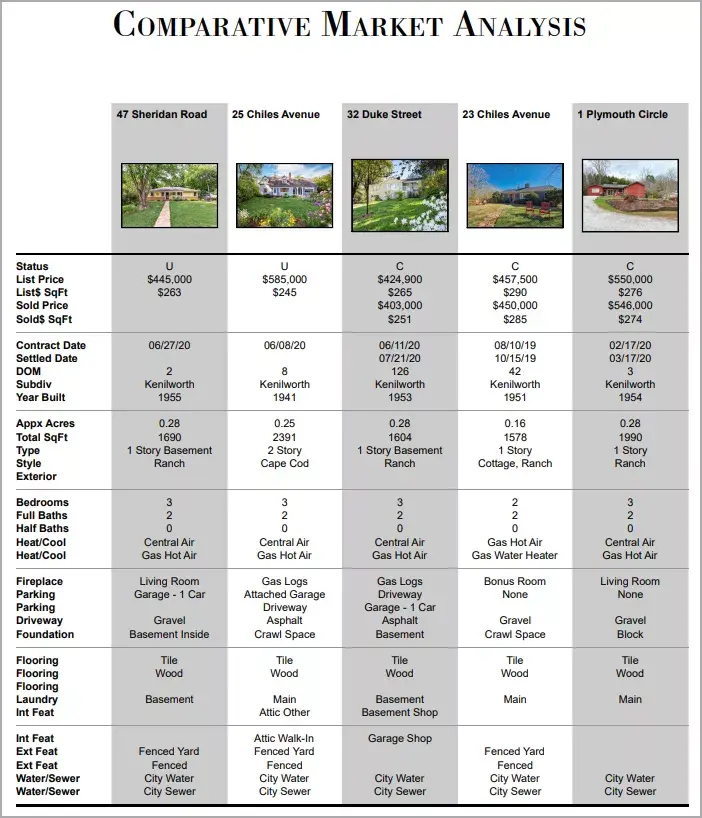
Credit: Investopedia
After choosing the comps, you’ll want to figure out the average price per square foot for each property (include the one you’re interested in). The equation you’ll need to use is simple:
Price / Square Footage
Step 4: Note the Differences and Make Adjustments
In this step, you’ll want to figure out the differences and take note. These differences can vary significantly, but even small differences may make a difference in overall price. For example, if a comp doesn’t have a half bath and the one you want does, you’ll need to add the value of the half bath to the estimated value of the property you want.
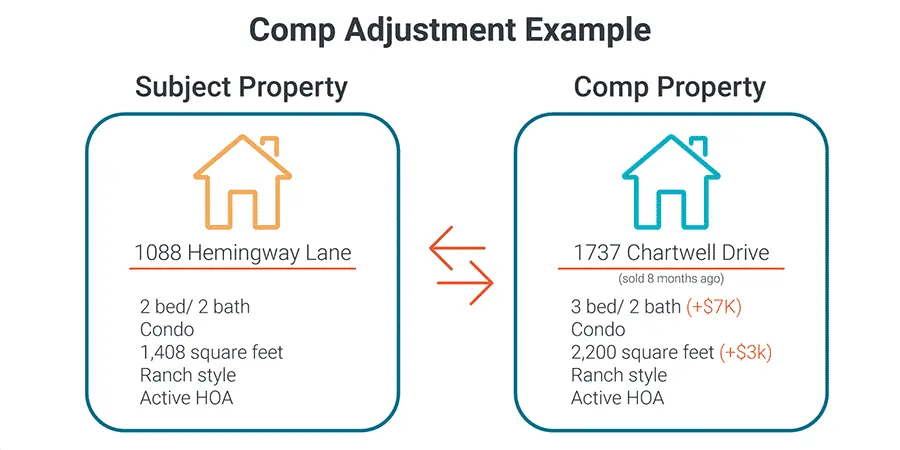
Credit: The Close
After figuring out the square footage and making adjustments, you can look back over the CMA and determine if the prospective property is, indeed, a good buy.
Note: Remember to find comps that are as similar to the property you’re interested in as you can get. This will make figuring out the average price per square foot much easier.
You’ve decided that, yes, you are ready to invest in real estate and you’ve even determined a property to be a worthwhile investment. Now it’s time to secure that financing!
“There are many ways to invest in real estate and there are many perks associated with it. Investment property financing takes several forms and the borrowers must meet specific criteria,” Mr. Capozzolo says.
Let’s take a look at traditional ways people can finance an investment property.
More than 78% of new homes purchased in the first quarter of 2022 were done with the help of a conventional loan serviced by a private lender, like a bank or a credit union. These loans are not backed by a government agency, but they may follow the guidelines put in place by Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac (which would mean they are a conforming loan).
|
Minimum Requirements to Qualify for a Conventional Loan |
|||
|
Credit Score |
DTI Ratio |
Down Payment |
Loan Term |
|
624 to 640 |
36% to 50% |
|
15-, 20-, 30-year |
The Federal Housing Finance Agency sets a limit on how much borrowers of a conforming loan can borrow every year.
|
2022 Loan Limits for a Conventional Loan |
|||
|
One-Unit Limit |
Two-Unit Limit |
Three-Unit Limit |
Four-Unit Limit |
|
$647,200 |
$828,700 |
$1,001,650 |
$1,244,850 |
“Conventional financing requires a down payment of 20% of the property’s purchase price. However, with an investment property, the lender may require 30%. A larger down payment could be a strong incentive and also provides the lender with greater security.” Mr. Capozzolo notes.
If you need a loan larger than the conforming loan limits, a jumbo loan is an option. Mr. Capozzolo explains:
“A jumbo loan is designed for higher-end expensive properties that are not covered by conventional loans. A jumbo mortgage can give prospective buyers larger funds, provided that they can find a lender that offers one and meets the requirements. The conforming loan limit set by the Federal Housing Finance Agency (FHFA) is limited to $647,000 for the conventional loan.”
|
Minimum Requirements for Jumbo Loans |
|||
|
Credit Score |
DTI Ratio |
Minimum Down Payment |
Cash Reserves |
|
700 and up |
45% or less |
Some lenders may require a cash reserve of 12-months of mortgage payments |
|
A fix and flip loan is geared toward investors who aren’t going to buy-and-hold their investments. These loans are perfect for those who are using the BRRR strategy and plan on selling their newly renovated property within 12 to 18 months.
|
Fix and Flip Loans vs Traditional Home Loans |
||
|
|
Fix and Flip Loans |
Traditional Loans |
|
Loan Term |
6 to 18 months |
15 to 30 years |
|
Interest Rates |
12% to 18% |
2% to 4% |
|
Purpose |
Short-term investment |
Long-term investment |
|
Collateral |
The investment property |
Borrower’s credit and property |
Typically these loans are used to purchase residential properties from homeowners who want to sell before the foreclosure process begins, but the loans can also be used to fund house rehab costs, and other expenses you might incur when you manage a rental property.
When you take out a home equity loan, you’re using your home as collateral and the amount you can borrow is determined by the value of your home. With this type of loan, you’ll receive a large, lump sum of money that you can use however you see fit.
|
Minimum Requirements for a Home Equity Loan |
|||
|
Credit Score |
DTI Ratio |
Equity in Home |
Loan Term |
|
620 and up |
No higher than 43% |
At least 15% to 20% |
5- to 30-years |
After receiving your loan amount, you’ll need to consider the terms of repayment because it will impact how much total interest will be paid. We recommend working out a monthly budget to see how much you can comfortably repay each month. See the example below:
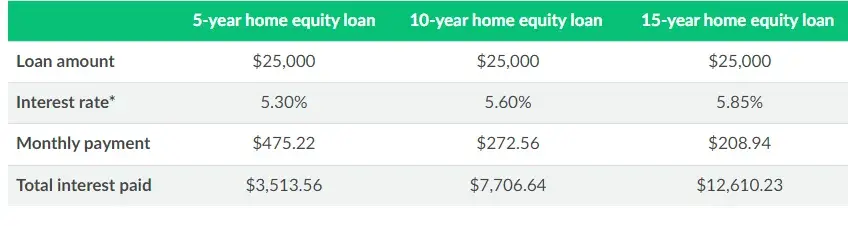
Credit: Lending Tree
*Rates are from 2021 and are used for examples only.
Rates as of September 2022:
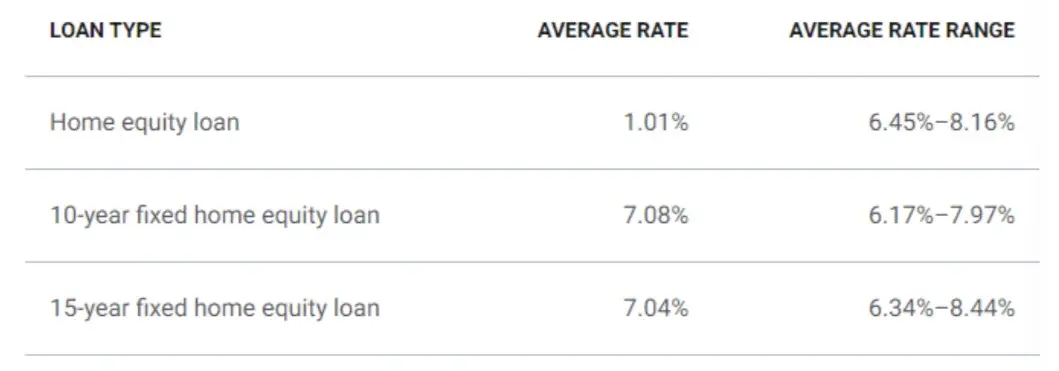
Credit: Bankrate
A HELOC, on the other hand, is very much like a home equity loan in that HELOC’s have the same minimum requirements as a home equity loan. However, there are a few differences between the two, as Mr. Capozzolo explains:
“A home equity line of credit (HELOC) allows you to draw funds as needed instead of a lump sum. HELOCs exhibit lower interest rates than home equity loans. However, the rates are variable and you might end up paying a higher interest rate in the near future.”
|
Home Equity Loan vs Home Equity Line of Credit vs Cash-Out Refinance |
|
|
Home Equity Loan |
HELOC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Like the previous two, your home and its equity will be key factors in how much you’ll qualify with a cash-out refinance.
A cash-out refinance is designed to replace your old mortgage with a new one that’s higher than what was owed on the old mortgage note. This option allows borrowers to get cash from their mortgages. Lenders will look at your property’s LTV ratio, credit history, and bank standards to determine how much money you’ll receive.
|
Minimum Requirements for a Cash-out Refinance |
|||
|
Credit Score |
Cash Reserves |
LTV Ratio |
Waiting Period |
|
680 and up |
At least 12 months’ worth of mortgage payments |
25%or more |
Must wait six months to refinance after the property was purchased |
|
When Does It Make Sense to Take: |
|||
|
|
Home Equity Loan |
HELOC |
Cash-out Refinance |
|
You Want: |
|
|
|
|
You Have: |
|
|
|
|
You Want: |
|
|
|
|
You Can: |
|
|
|
|
You Want to: |
|
|
|
If you need cash in your hand right now, a hard money loan is the way to go. However, they can be predatory because in exchange for getting cash within a few days of approval, you’ll be slapped with a high interest rate. Also, these loans aren’t financed by a bank or credit union — they’re typically financed by financing companies, individual investors, or investing groups.
|
Minimum Requirements for a Hard Money Loan |
|||
|
Interest Rate |
Processing Time |
Minimum Down Payment |
Loan Terms |
|
10% -15% |
1 – 2 Weeks |
70% LTV x ARV |
12- to 36-months |
Mr. Capozzolo: “Hard money and private lenders are quite helpful when it comes to financing investment properties. Their conditions are more flexible than conventional lenders and they work with all types of borrowers. Qualifying for an investment property loan is challenging as lenders view investment properties to exhibit greater risk. Lenders expect a larger down payment for investment properties, generally between 20% to 35%.”
Taking out a loan through a private lender is much like a hard money loan in that there’s a faster processing time, there’s no minimum credit score requirements, and there’s more repayment flexibility. Since private money lenders are usually a singular individual or an organization unaffiliated with any banking institution, each lender can set their own requirements and terms for repayment.
|
Hard Money Loans vs Private Money Loans |
||
|
|
Hard Money Loans |
Private Money Loans |
|
Credit Requirements |
|
|
|
Repayment |
|
|
|
Collateral |
|
|
|
Flexibility |
|
|
|
Loan Terms |
|
|
|
Property Type |
|
|
Borrowers can secure peer-to-peer loans by going to an online platform like Prosper, Peerform, or Funding Circle. These platforms connect investors who can supply the funds borrowers ask for. The online platform will coordinate the loan, transfer the funds from the lender to the borrower, and will repay the investor when the borrower makes a payment.
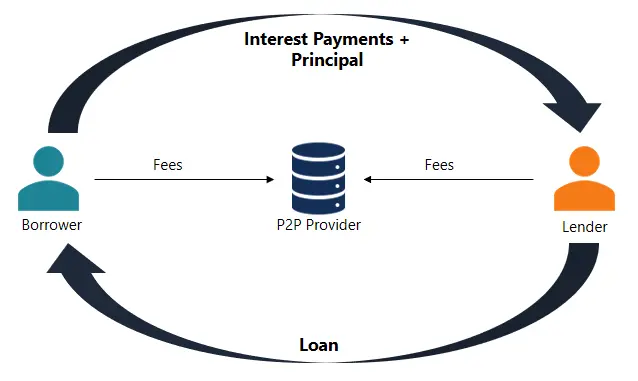
Credit: Corporate Finance Institute
Each peer-to-peer lending platform will have their own borrower requirements, so it’s strongly recommended to compare platforms before signing with anyone.
Note: Peer-to-peer lenders can be regular folks who want to grow their money though the borrower’s interest payments.
Technically speaking, FHA and VA loans cannot be used to buy investment properties because the funds can only be used to purchase a primary residence. They’re designed to help low- and moderate-income buyers buy a home without having to put down a large down payment.
If the loans are intended for borrower’s to purchase a primary residence, how can the funds be used for investment properties? Two words: owner occupancy.
You can purchase a multifamily home with two, three, or four units, as long as you intend on living in one of the units and renting the remaining. This is called house hacking. So while you’re collecting rent from the units that you’re not living in, you’re paying down your mortgage, building equity, and dipping your toe in real estate investing if this is your first investment.
|
|
FHA Loans |
VA Loans |
|
Credit Score |
500 |
No minimum score |
|
Down Payment |
|
$0 |
|
DTI Ratio |
50% or less |
41% or less |
|
Income Requirements |
|
|
|
FHA Loan Limits |
|
Must meet VA’s minimum property requirements |
A FHA 203(k) loan is a loan that will allow borrowers to purchase flip houses for sale and add the cost of repairs into the mortgage. There are two types of 203(k) loans available:
|
Minimum Requirements for a FHA 203(k) Loan |
|||
|
Credit Score |
DTI Ratio |
Minimum Down Payment |
Other Considerations |
|
500 and up |
43% or less |
|
Renovations and repairs must be done by a licensed contractor — not the borrower |
With a limited 203(k) loan, there is no minimum improvement cost, but you cannot exceed $35,000 in improvement costs. A standard 203(k) loan has a $5,000 minimum improvement cost. The maximum improvement cost must be the lesser of either the purchase price plus renovation costs or 110% of the ARV.
Out-of-Pocket Expenses: Since you can only borrow as much as the property’s ARV, you might have to pay out of pocket for unexpected costs.

Unlock access to our exclusive inventory of off-market investment properties.
Business isn’t about deals. It’s about relationships and we’d love to begin one with you. Interested in buying a property? Have a question about our process? Curious about a local market? Let’s talk.
There are a lot of conventional loan options for financing an investment property, but there are also some non-conventional options that might work for your specific needs.
Under seller financing, the investor will pay the homeowner in installments until the purchase price has been paid off.
With this type of financing, you won’t have to pay in cash right off the bat or take out a mortgage. Since this arrangement is made between the investor and the homeowner, the terms can be negotiated to suit both parties.
There are four primary ways seller financing agreements can be structured:
Unlike conventional mortgage lenders, a portfolio loan will stay with the servicer instead of being sold off to an entity like Fannie Mae or Freddie Mac. By keeping the loan, the lender can customize the underwriting requirements. Consequently, this means each lender may have their own guidelines.
|
Minimum Requirements for a Portfolio Loan |
|||
|
Credit Score |
DTI Ratio |
Minimum Down Payment |
Loan terms |
|
Varies by lender |
43% or less |
3% to 25% for better terms |
10-years or less |
Portfolio loans are ideal for people who have experienced divorce, bankruptcy, or a previous foreclosure — all of which can be damaging to your credit history.
The trade-off for the flexibility of these loans, lenders may tack on higher interest rates, higher origination fees, and include prepayment penalties in the contract.
A land contract is a form of seller financing in that the deal is conducted between the investor and the seller.
The seller will agree to finance the property if the investor agrees to certain terms. Since the deal is between the seller and investor, the terms can vary widely from seller to seller.
That said, with these types of contracts, the seller will keep the legal title until the land contract is paid in full.
As the investor is paying off the contract, they are building equity by way of an equitable title. This can be beneficial if the investor wanted to pay off the contract by getting a traditional mortgage.

Unlock access to our exclusive inventory of off-market investment properties.
Business isn’t about deals. It’s about relationships and we’d love to begin one with you. Interested in buying a property? Have a question about our process? Curious about a local market? Let’s talk.
If this is your first time applying for financing, then you’re probably not going to know the ins and outs that’ll lead to a smooth application process. Don’t worry — we got your back.
Here are some useful tips that’ll help you get everything in order so that when you do submit your application, you’ll have a better chance of being approved.
Mr. Capozzolo advises: “Aspiring investors must be aware of the pros, cons, and due diligence associated from beginning to end. 21% of aspiring investors show their cards by not being aware of the market conditions.”
“My professional advice would be to conduct research and due diligence in depth regarding the investment property, physical features, market growth, and future trends. They must also be aware of who they are getting into business with. Around 10% of new investors don’t take verifying the other party into heed and end up on the wrong side of the business.”
Your credit score and credit report is an important, perhaps the most important, factor lenders look at when determining your creditworthiness.
It impacts the interest rate you’ll get, what type of loans you qualify for (if any), and repayment terms. The minimum credit score most lenders will work with is 620, but you can find some lenders who’ll work with borrowers with poor credit.
You can get a free credit report from all three credit unions by going to AnnualCreditReport.com. You’ll be able to review your full credit report, check for inaccuracies and dispute anything that you don’t recognize as your debt.
Between now and when you actually receive the funds, keep paying your bills on time, don’t take out any more debt or incur a lot of credit card debt, and don’t quit your job!
If your DTI ratio is higher than 40% (yes, 43% is the industry standard, but it’s always better to be safe with a lower DTI than to be sorry), you’ll want to work on paying down that debt.
Some ways you can pay off your debt quickly include:
Sometimes lenders will require that you have a sizable amount of cash in savings in case of an emergency. The amount of cash reserves you’ll want to have will depend on your investment goals, your budget, and the type of loan you’re trying to get approved for.
Some lenders only require three months of mortgage payments worth of savings, while others will require a full year’s worth of mortgage payments. Experts, on the other hand, recommend having three to six month’s worth of total living expenses on reserve.
In order to apply for a loan, you first need to know how much you can afford to borrow. Housing is the largest monthly bill that Americans have — it’s recommended that no more than 30% of your gross monthly income goes to housing, but on average, that figure is more around 35% (or more!) on average.
When you’re trying to figure out how much you can afford to borrow, you’ll need to consider upfront costs and recurring costs.
Upfront Costs:
Recurring Costs:
Most lenders will require that you provide them with a bunch of documents for them to review with your application. The most common documents you’ll need to supply include:
Did you know that there’s a 14-day window where you can apply for loans with different lenders without hurting your credit score? When you submit mortgage applications with different lenders in that period, it will only show as a single hard credit inquiry.
That said, you’ll want to shop around for a mortgage to find the lender with the best terms. Some lenders will have more relaxed qualification requirements, while others may offer lower interest rates. This is your chance to cast your net wide!
As you hear back from lenders, don’t go with the first one who says that you’ve been approved. You’ll want to go through the offers to see which lender has offered the best terms. Pay close attention to interest rates, closing costs, and prepayment penalties.
The percentage lenders use to determine how much of your monthly income goes toward making debt payments. You can use a DTI calculator to figure this out or use the equation:
(Total Monthly Debt) / (Gross Income) x 100 = DTI
To protect themselves, some conventional loan servicers may require that you take out a private mortgage insurance (PMI) if you don’t have an adequate down payment. Sometimes PMI is paid in one lump sum at closing, but usually the premium is rolled into your monthly mortgage payment.
You can use a PMI calculator to determine how much you’ll pay over the life of the loan. However, once you have accrued 20% equity in the property, you can remove the PMI, thus saving you a little bit of money.
Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac are organizations that were created by Congress to “provide liquidity, stability, and affordability to the mortgage market.” These organizations buy mortgages from lenders and will either hold them or resell them as mortgage-backed securities.
A conforming loan meets guidelines set by Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac, but they aren’t backed by the federal government. Conforming loans are readily available and they often have lower interest rates and fees. That said, to qualify for these loans, a borrower must have good credit and a low DTI ratio.
A non-conforming loan does not follow the guidelines set by Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac. These loans typically exceed the maximum loan limit for an area; but, there are other reasons a loan could be considered non-conforming, like being backed by the government like FHA, VA, and USDA loans.
This is a term often used by investors who buy flip houses or use the BRRRR method of real estate investing to figure out the property’s value after renovations have been completed. The ARV is also used to secure certain types of loans.
You can use an ARV calculator to figure out the property’s ARV value or you can use this equation:
Property’s Current Value + Value of Renovations = ARV
ARV can also be used by investors when they’re submitting an offer on a property that needs work. They use something called the 70% rule where they will use the ARV and cost to make the necessary repairs to come up with their offering price.
You can use a 70% calculator to figure out your maximum offer price or use this equation:
(ARV x 70%) – Estimated Cost for Repairs = Maximum Offer Price
When applying for a home equity loan, HELOC, or cash-out refinance, lenders will use this ratio to determine the amount of risk they’ll take on should you default. Higher LTV ratios won’t disqualify you from being approved for funding, but you will have a higher interest rate and may need PMI.
You can use an LTV Ratio calculator to figure out the LTV ratio on your property, or you can use this equation:
Mortgage Amount / Appraised Property Value = LTV Ratio
The very first step in becoming a successful real estate investor is deciding that you’re ready to dive in without any reservations.
You can’t go into this business half-hearted and unknowledgeable because it’s very likely that you’ll make mistakes that could cost you a lot, financially, mentally, and professionally. It’s not a decision that should be taken lightly.
After taking the time to really think about your goals and how you’d like to achieve them, you’ll want to look into the area that you’d like to begin investing in.
By researching the local market, you’ll be able to see what properties are being sold for, how active the market is, and there’s a demand for rental properties. Fortunately, that’s not an issue considering 36% of households in the United States are renters. Even if you prefer to fix and flip, the demand for housing is there.
Once you find the area you’d like to begin investing in and you’ve found an investment opportunity, you need to figure out which financing option is right for your situation.
There are many options out there and it’s in your best interest to research all of your options before making any concrete plans because you don’t want to fall victim to predatory lenders who will foist high interest rates and strict repayment conditions on you.
Our goal with this guide was to provide you with easy to digest information regarding the different financing options available to new investors.
If you need some more in-depth advice about how to finance an investment property or have questions about investments in general, you can always count on New Western’s experts for great advice.

Unlock access to our exclusive inventory of off-market investment properties.
Business isn’t about deals. It’s about relationships and we’d love to begin one with you. Interested in buying a property? Have a question about our process? Curious about a local market? Let’s talk.
Disclaimer: The information provided on this website does not, and is not intended to, constitute legal advice; instead, all information, content, and materials available on this site are for general informational purposes only.